
The Golden Age of Technology
While technology is in its golden age, it is a fact that some developments outshine others. Although it is not entirely possible to foresee which innovations will dominate our lives in the future, today’s “trends” help us make certain predictions. Here are some of today’s technologies that were once thought to be just “science fiction” –and we will possibly be even more intertwined in the near future.
VR + AR = MR
Virtual Reality (VR) made it possible for us to visit places that are far away or non-existent; Augmented Reality (AR) helped us add data, information and virtual interaction into our environment; and now we’re ready for Mixed Reality, a combination of the two.
Mixed reality can be summarized as creating fully digital objects that are interactive and observable in the user’s physical environment. Users can view [from different angles] and change complicated things, such as an anatomical model or machine parts.
The recently announced Magic Leap, Microsoft’s HoloLens, and Google Glass, which achieved success in the commercial environment despite having problems in the consumer market show that mixed reality has already become an indispensable technology in commercial and industrial environments, if not in our immediate surroundings.
A survey conducted by Toshiba in May 2018 revealed that 82% of enterprises predict “AR smart glasses” -or mixed reality- will be adopted in their operations in the next three years.
In the automotive industry, and in companies producing similar dangerous engines or machinery-based structures, it is a great advantage to be able to see the desired end-products with minimum expense and minimum danger.
These hands-free, headset-based systems are also helpful for customers from various branches, from doctors to automobile assemblers. Training videos, labeled images, and quality assurance checklists are easily accessible to ensure that jobs are done safely and quickly. Goggles can also connect you with your colleagues, so you can observe what others see in a live video stream for real-time collaboration and troubleshooting.

Of course, these are commercial applications. Mixed reality can also add magic to our daily lives. MR allows us to write our own rules about how people perceive the world and
how they react to it. When you combine physical and digital elements in unexpected ways, the entertainment possibilities you can create seem infinite.
Cloud computing, Edge computing, and the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system in which interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) have the ability to transfer data over a network with no requirement for a human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
Edge Computing is simply the next version of cloud computing.
In cloud computing, we tend to upload, process, and download our data on geographically remote clouds or servers. This system greatly decelerates uploading and downloading data.
However, in edge computing, servers are located close to our geographic location. This substantially speeds up data transfer. From the point of view of the Internet of Things, processing of raw data produced by its devices in a closer location, rather than transferring them to data centres or clouds over long paths, provides a great advantage in terms of speed, convenience, and data transfer fees.
For example, a security camera can use on-device vision processing to track motion, distinguish family members, and send alerts only if someone is unrecognized or cannot fit into predefined parameters. It reduces the amount of bandwidth, cloud processing, and cloud storage used against the alternative of sending raw video streaming over the network by performing vision tasks with the on-board computer. In addition, on-device processing increases the speed of alerts while reducing the likelihood of annoying, repetitive false alarms.
Edge devices are being built with increasingly complex computing capabilities. Coupled with advanced connectivity technologies such as 5G that will enable faster and more robust connectivity, we are obviously on the verge of witnessing the birth of a new type of smart devices and applications.
Blockchain
Blockchain was invented in 2008 by a person (or a group of people) using the alias Satoshi Nakamoto to serve as the public trading book of the cryptocurrency Bitcoin.
A blockchain is a serial data record, which carries a non-modifiable timestamp, distributed and managed by clusters of the computer. It enables the creation of decentralized databases that are resistant to censorship, and that potentially allow the adoption of this system in critical applications such as finance and identity.
It is the safest technology for financial transactions due to its decentralized nature and authenticity. Like many cryptocurrencies, Facebook’s new Libra cryptocurrency also uses blockchain technology.
It has helped many industry leaders to achieve significant business benefits such as greater transparency, increased security, increased traceability, operation efficiency, and cost-saving.

Experts believe that the ability to keep all transactions unalterable and transparently recorded will soon make blockchain technology used in all areas, rather than just in financial transactions.
Due to various technical problems such as poor scalability and interoperability, blockchain is still not fully mature for business applications. However, it has the potential to reshape all industries by promoting trust, transparency, and value exchange in business ecosystems.
Some of its major uses will possibly be asset tracking, automated demand processing, internal and common record-keeping, smart cities, and the Internet of Things.
3D printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating any three-dimensional object by the layering of raw material based on a digital file.
In a 3D printer, one or more printheads operate by compressing a small amount of material in precise locations to create objects at specific points in a top-down fashion.
Today, we are able to produce full-colour 3D print-outs by using around 250 different materials including titanium, rubber, plastic, glass, ceramics, leather, and even chocolate!
This system is already regarded as the most important technology in the future. Here are the latest developments in this field, and the advances expected soon:
Print-outs from over 250 different materials and with full-colour unfold opportunities we have never seen before. Material mixtures and the use of millions of shades of colour in the same print are inevitable and quite open-ended in terms of development.
In the medical field, 3D printing is subjected to major developments. In addition to printing personalized knee and hip bones, it is also crucial to be able to use personalized guides and cutting tools in these operations. Also in hearing aids, 3D printing that perfectly fits the patient’s ear canal has long been a great comfort.
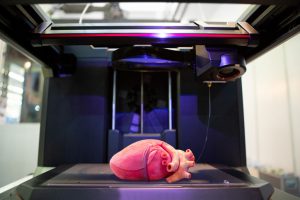
The acceleration of 3D printing means more people and organizations joining the trend, in industrial and personal terms. If we can get the result in minutes instead of spending an entire day waiting for a tiny piece, everyone will want to benefit from it. 3D printing speed is expected to increase by 100 times in the next 5 years.
With the development of printers using metal, get ready to see 3D-printed jewelry, car and aircraft parts, kitchenware, and prototypes. 3D metal printers will not only eliminate waste in manufacturing but can also produce lighter parts; this is a very important development, especially for the aircraft industry. Today, more than 20 different alloys can be used for printing. Companies such as General Electrics and SpaceX produce parts of jet and rocket engines by 3D printing.
This feature has the potential for billions of dollars in industrial applications for 3D printing. In the future, while applications such as the preparation of meals containing tailor-made nutrients and quantities are already expected, 3D-printed pills containing the required quantities of ingredients according to your daily needs will revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry.
The researchers have convincingly demonstrated that simple organs and complex tissues can now be printed in 3D. By collecting and replicating our own stem cells, we may then place these miraculous cells on a collagen scaffold of any desired organ to transform them into a fully transplantable, functional organ.
REFERENCES
- 1. https://singularityhub.com/2019/04/08/5-big-breakthroughs-to-anticipate-in-3d-printing/
- 2. https://www.forbes.com/sites/solrogers/2018/12/04/what-is-mixed-reality-and-what-does-it-mean-for-enterprise/#758f5ace5df9
- 3. https://www.crn.com/news/internet-of-things/blockchain-5-things-the-channel-needs-to-know?itc=refresh
- 4. https://www.networkworld.com/article/3234708/why-edge-computing-is-critical-for-the-iot.html
