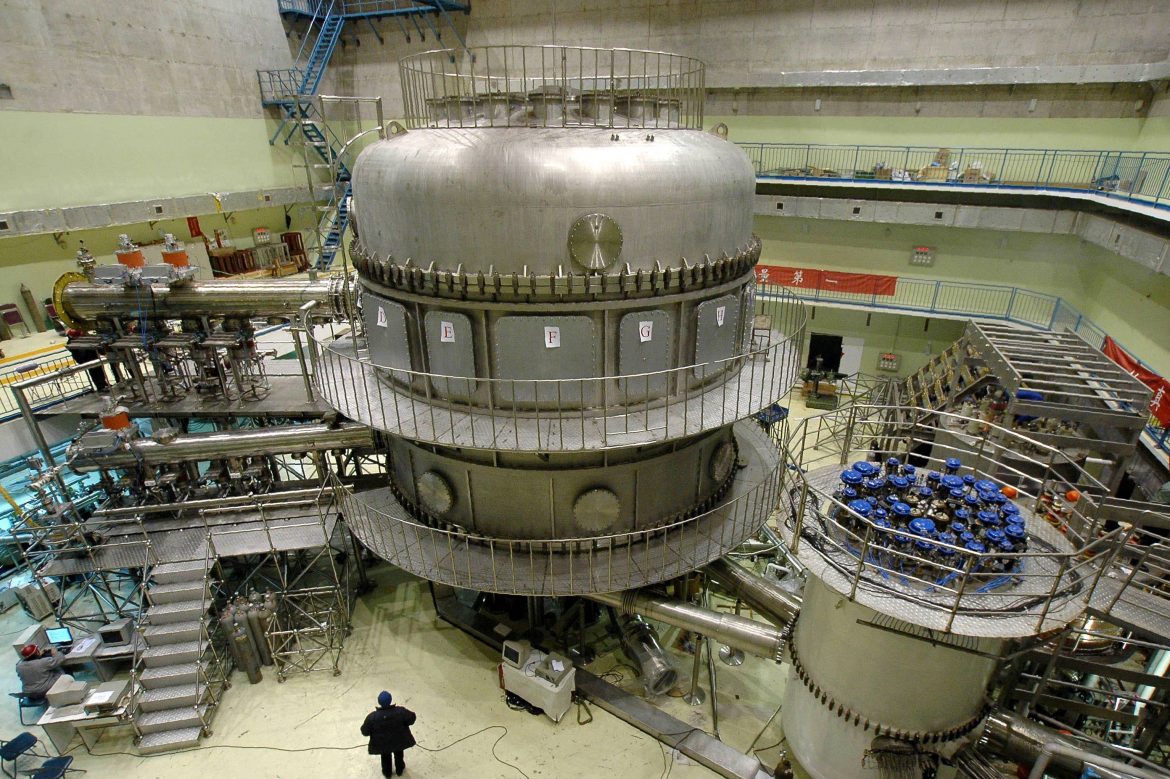
Hotter Than the Sun
China’s experimental superconductor tokamak fusion reactor (EAST) broke a record by reaching 100 million degrees Celsius of core temperature, which more than six times hotter than the Sun. This experiment brings us one step closer in generating clean energy by using nuclear fusion.
Tokamak type reactors operate by bringing hydrogen isotopes (and usually deuterium) to very high temperatures until they become plasma, compressing this plasma between a series of powerful magnets inside a toroidal (ring-shaped) chamber, and forcing some nuclei to fuse. This system, in principle, works similar to the reaction inside the Sun’s core. Because the generated energy yields by-products that are not radioactive, the system is regarded as the safest option of clean energy for the Earth.
EAST reactor produced this record temperature by heating hydrogen atoms injected into the ring-shaped chamber with four different methods to create the plasma, and sparking the fusion process by squeezing this plasma with superconducting magnets. The resulting Sun-like environment facilitated the fusion of hydrogen atoms, yielding an enormous amount of energy. Although EAST was able to keep this temperature for only 10 seconds.
The main goal of scientists in these experiments is to create a self-maintaining fusion environment and ensuring that the reactor generates more than energy than it consumes.
REFERENCES
- 1. https://newatlas.com/fusion-china-artificial-sun-east/57237/
- 2. https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/280684-chinese-fusion-reactor-gets-6-times-hotter-than-the-sun
