Pull The Plug on The Noise
With the increase of urbanization, types and levels of noise have been increasing day by day. As a result of this environmental problem, public health has been negatively affected, and continues to be neglected in many parts of the world. But how can we overcome this massive issue? Currently, researchers who work on acoustics offer a solution called “Active noise control” to block unwanted sounds. While the beginnings of the technology date back to 1935, from the 2000s, the application areas of this unique concept have increased. Now, it has entered many fields of our lives. In this article, I introduce noise reduction methods, and active and passive noise control measures, as well as answer basic questions about the subject.
First of all, let’s examine the methods used to reduce noise. The most effective method in controlling unwanted sound is to take mitigation measures at the source. However, control at the source is a challenging task for environmental noise as many stakeholders are involved, for example, independent manufacturers, government bodies, and individuals. Alternatively, noises can be blocked along the sound propagation path and at the point of the receivers. Noise barriers and façade shielding are examples of blocking sounds in the propagation path. Lastly, noise can be controlled at the receiver by using headphones. These noise reduction methods can be carried out with two different techniques, passive noise control and active noise control.
What is passive noise control (PNC)?
The PNC technique reduces noise by using the material’s chemistry. The materials used in PNC have acoustic properties which provide absorption, diffusion or reflection of sound. PNC performs better at high frequencies and does not require electric power. On the other hand, since most of the passive materials block airflow, heat management must be considered in some applications such as engine-related exhaustion. Due to the nature of passive materials, they must be thick to provide noise reduction at low frequencies, which makes them bulky. Nonetheless, PNC has been widely used in many diverse areas due to their cost-effectiveness and relatively scalability. Although this passive method has some advantages, such as simplicity and does not require power, it generally restricts the airflow and is not effective for low-frequency sounds. As an alternative to passive methods, active mitigation methods, also known as ANC can overcome these issues.
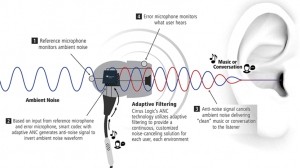
Differences between active and passive noise control
ANC generates an acoustic wave that can mitigate low frequencies more efficiently. Also, it reduces low-frequency sounds with a much thinner structure than PNC. Therefore the noise-cancelling system takes up less space and is lighter, making compact designs easily achieved. However, ANC also has some shortcomings. One of the most significant disadvantages is its requirement for electrical power. They require an application-specific design to get the best performance. Its high cost and risk of noise spillover are other downsides.
In conclusion, both systems have unique properties with positive and negative elements. The best results can be obtained by combining the different frequency ranges in which these two systems are effective. In this way, unwanted sounds may be blocked efficiently in one device. Although there have been countless applications of PNC that we can easily see in our daily lives, ANC has not yet been widely adopted. Furthermore, some new research findings suggest that the utilization of artificial intelligence may help fill these gaps in their practice of ANC. In this way, ANC systems can be widely utilized in a noisy environment and help us live a more comfortable life.
REFERENCES
- 1. Lam, B., Gan, W. S., Shi, D., Nishimura, M., & Elliott, S. (2021). Ten questions concerning active noise control in the built environment. Building and Environment, 200, 107928.
