Trees say so…
A new study by NASA scientists has shown that the drought affecting the region surrounding Eastern Mediterranean, also called Levant, is the worst of last 900 years. Besides Turkey, the drought-hit area also covers Cyprus, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine and Syra.
The research, led by Ben Cook at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies and to be published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, a publication of the American Geophysical Union, is based on the study of tree-ring records in the countries of the region. The concentric rings seen in cross sections of felled trees show how much the tree has grown each year.
The thickness of the rings added every year is an indicator of the amount of water available each year for its growth. Thick rings attest to humid years with an abundance of water stimulating robust growth, and the thin ones mark the times of drought.
Going through the data showing the growth progress of tree rings in the period spanning just over 900 years from 1100 to 2012 contained in the Old World Drought Atlas (OWDA), researchers concluded that the drought which affected the region in the 15-year period from 1998 to 2012 was the worst of the past nine centuries. According to the findings, the drought prevalent in the region during that time was 50 percent heavier than the worst drought over the past 500 years and 10-20 percent heavier than the worst of the past 900 years.
The results also overlap with an earlier study which links the current civil war with a drought that hit the countries in the “fertile crescent”, or Mesopotamia at about the same time. (See: https://kurious.ku.edu.tr/sites/kurious.ku.edu.tr/files//drought_may_have_ignited_syria_war.pdf )
The researchers in the NASA study have also identified some patterns in the rising drought trends as a result of the human caused global warming.
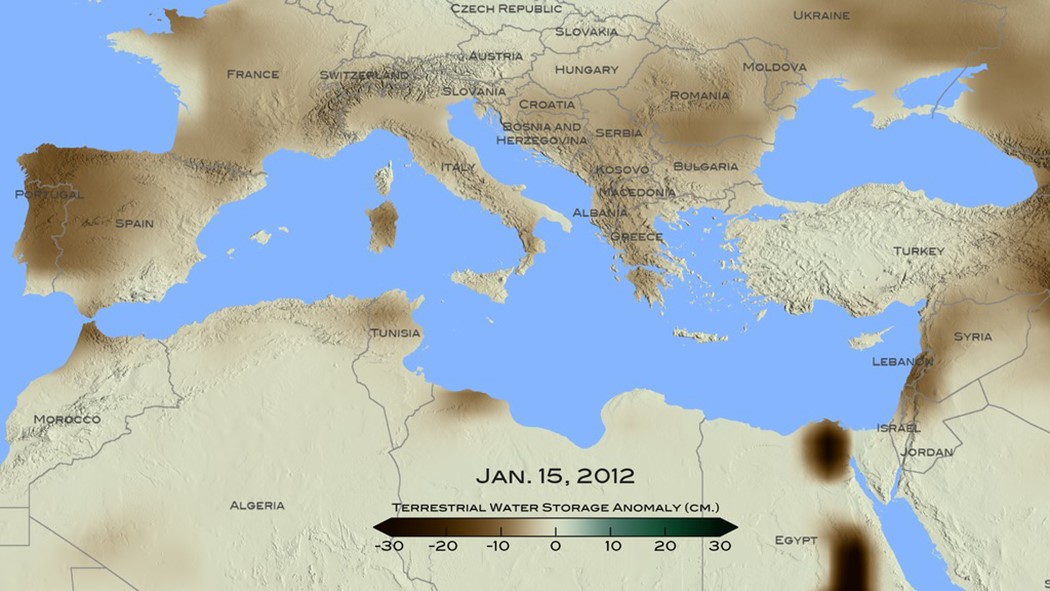
Whereas the droughts prevalent in the Eastern Mediterranean Basin also affect Western Mediterranean, the anomaly in precipitation displays itself at Northern Mediterranean and the Black Sea as heavier than average rainfall.
According to the study, the regime of precipitation is heavily influenced by two air flow cycles named North Atlantic Oscillation and the East Atlantic System. These systems drive warmer and drier air masses to the Mediterranean in cycles linked with currents and temperatures in the ocean, which in turn speed up the evaporation in the soil, leading to terms of drought.
REFERENCES
- 1. “NASA finds drought in Eastern Mediterranean worst of past 900 years”, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, 1 March 2016